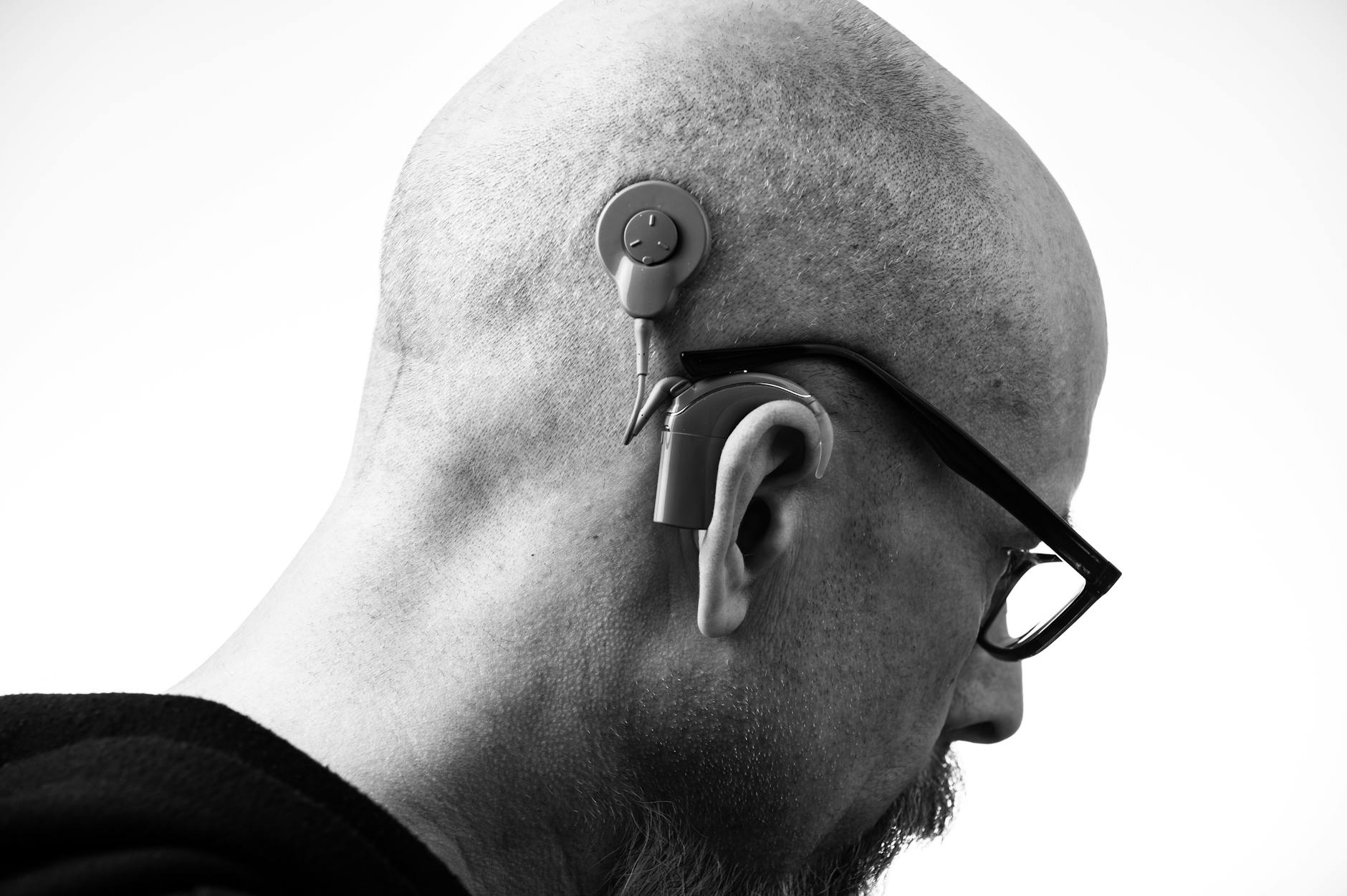
Hearing loss affects millions of people worldwide, but understanding the different types can help you make informed decisions about your hearing health. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the various forms of hearing loss, their causes, and available treatment options.
Types of Hearing Loss
There are three main types of hearing loss, each affecting different parts of the ear and requiring different treatment approaches:
1. Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound waves cannot efficiently travel through the outer or middle ear. This type of hearing loss often results from:
- Earwax buildup or blockage
- Fluid in the middle ear from colds or infections
- Ear infections (otitis media)
- Perforated eardrum
- Problems with the tiny bones in the middle ear
The good news is that conductive hearing loss is often temporary and treatable through medical intervention or minor surgical procedures.
2. Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type, accounting for about 90% of all hearing loss cases. It occurs when there's damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or the auditory nerve pathways. Common causes include:
- Age-related hearing loss (presbycusis)
- Noise-induced hearing loss
- Genetic factors
- Certain medications (ototoxic drugs)
- Head trauma
- Viral infections
Unlike conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss is typically permanent. However, hearing aids and cochlear implants can significantly improve hearing ability and quality of life.
3. Mixed Hearing Loss
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss. This means there are problems in both the outer/middle ear and the inner ear or auditory nerve. Treatment typically involves addressing both components of the hearing loss.
Degrees of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is also classified by severity, measured in decibels (dB):
- Mild (26-40 dB): Difficulty hearing soft sounds and speech in noisy environments
- Moderate (41-70 dB): Difficulty hearing normal conversation levels
- Severe (71-90 dB): Can only hear loud sounds and speech
- Profound (91+ dB): Can only hear very loud sounds, may rely on visual cues
Signs and Symptoms
Recognizing the early signs of hearing loss is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Frequently asking others to repeat themselves
- Turning up the volume on TV or radio
- Difficulty following conversations in noisy environments
- Feeling like others are mumbling
- Avoiding social situations due to hearing difficulties
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
"Early detection and treatment of hearing loss can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life. Don't wait if you're experiencing symptoms – consult with a hearing healthcare professional today."
Treatment Options
The treatment for hearing loss depends on the type, severity, and underlying cause:
Medical Treatment
For conductive hearing loss, medical treatments may include:
- Earwax removal
- Treatment of ear infections
- Surgical repair of the eardrum or middle ear bones
Hearing Aids
Modern hearing aids are sophisticated devices that can significantly improve hearing for most types of hearing loss. They come in various styles and feature advanced technology like:
- Digital noise reduction
- Directional microphones
- Bluetooth connectivity
- Rechargeable batteries
Cochlear Implants
For severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss, cochlear implants may be recommended. These surgically implanted devices bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve.
Prevention and Protection
While not all hearing loss can be prevented, you can take steps to protect your hearing:
- Use ear protection in noisy environments
- Keep the volume at safe levels when using headphones
- Take breaks from loud noise exposure
- Get regular hearing checkups
- Maintain good ear hygiene
- Manage underlying health conditions
When to Seek Help
If you suspect you have hearing loss, don't delay in seeking professional help. An audiologist can perform comprehensive hearing tests to determine the type and degree of your hearing loss and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Remember, hearing loss is a common condition that affects people of all ages. With proper diagnosis and treatment, most people with hearing loss can continue to lead full, active lives.
References
- Hearing Loss - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
- Types of Hearing Loss | Hearing Loss in Children | CDC
- Hearing loss - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic
- About the Types of Hearing Loss | Parent Guides to Hearing Loss | CDC
- Deafness and hearing loss
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf